Technical Rate Of Substitution | The marginal rate of substitution cannot be used to determine consumer preference, though some companies try to use it in this manner. What is the marginal rate of technical substitution? Marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts) is the rate at which a firm can substitute capital with labor. Technical rate of substitution in consumption between x and r, reflected by the shape or the slope of indifference curves, provides additional information about an individual's preference for one good or another. In microeconomic theory, the marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts)—or technical rate of substitution (trs)—is the amount by which the quantity of one input has to be reduced (.
Technical rate of substitution in consumption between x and r, reflected by the shape or the slope of indifference curves, provides additional information about an individual's preference for one good or another. Marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts) is the rate at which a firm can substitute capital with labor. Marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts) is the rate at which a firm will substitute one input for another to be able to produce a fixed amount of output. In microeconomic theory, the marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts)—or technical rate of substitution (trs)—is the amount by which the an isoquant map where q3 > q2 > q1.at any point on any isoquant, the marginal rate of technical substitution is the absolute value of the slope of the. What is the marginal rate of technical substitution?

Iarginal ratc of technical substitution of x for y is the number of units of factor which can he replaced hy one unit if factor x. The rate at which one factor has to be decreased in order to retain the same level of productivity if another factor is increased. In microeconomic theory, the marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts)—or technical rate of substitution (trs)—is the amount by which the an isoquant map where q3 > q2 > q1.at any point on any isoquant, the marginal rate of technical substitution is the absolute value of the slope of the. In this paper, we introduce the concept of technical rate of substitution (trs). Marginal rate of substitution example. This is the marginal rate of technical substitution, the slope of the isoquant. In microeconomic theory, the marginal rate of technical substitution —or technical rate of substitution —is the amount by which the quantity of one input has to be reduced when for faster navigation, this iframe is preloading the wikiwand page for marginal rate of technical substitution. Technical rate of substitution measures the change in one input. In microeconomic theory, the marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts)—or technical rate of substitution (trs)—is the amount by which the quantity of one input has to be reduced (. As a result, the factor being tradeoff won't be able to make as much contribution as it should have for the efficient production. Causes of diminishing marginal rate of technical substitution. ), so that output remains constant. What is the marginal rate of technical substitution?
The marginal rate of substitution cannot be used to determine consumer preference, though some companies try to use it in this manner. Meanwhile, spectrum sharing techniques and utilization of higher frequency bands make more bandwidth available. Marginal rate of substitution example. Answered august 21, 2017 · author has 656 answers and 4.3m answer views. Occasionally, you may hear reference to the marginal rate of technical substitution, or mrts.

In microeconomic theory, the marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts)—or technical rate of substitution (trs)—is the amount by which the an isoquant map where q3 > q2 > q1.at any point on any isoquant, the marginal rate of technical substitution is the absolute value of the slope of the. Marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts) is the rate at which a firm will substitute one input for another to be able to produce a fixed amount of output. It has the same interpretation as any other slope. We reproduce below the same table to find out the marginal rate of technical substitution. In the second graph, both inputs are perfect substitutes, since the lines are parallel and the mrts = 1, that is the slope has an angle of 45º with each axis. Let us understand this using a diagram. In microeconomic theory, the marginal rate of technical substitution —or technical rate of substitution —is the amount by which the quantity of one input has to be reduced when for faster navigation, this iframe is preloading the wikiwand page for marginal rate of technical substitution. Technical rate of substitution in consumption between x and r, reflected by the shape or the slope of indifference curves, provides additional information about an individual's preference for one good or another. Technical rate of substitution measures the change in one input. Such change gets adjust in or to keep output constant. Substituting one factor for the other continuously causes scarcity of the factor being replaced. It means that the marginal rate of technical substitution of factor labor for factor capital (k) (mrtslk) is the number of units of factor capital (k) which can be the decline in mrts along an isoquant for producing the same level of output is named as diminishing marginal rates of technical education. There are number of firms which are doing the above equation shows the implicit function.
Meanwhile, spectrum sharing techniques and utilization of higher frequency bands make more bandwidth available. (a) find the marginal rate of technical substitution for the production functions using total differential to find the marginal rate of substitution. It can also be defined as the more complete name for the marginal rate of substitution between factors in a production function, sometimes used to. The marginal rate of substitution cannot be used to determine consumer preference, though some companies try to use it in this manner. The marginal rate of technical substitution shows the rate at which you can substitute one input, such as labor, for another input, such as capital, without changing the level of resulting output.
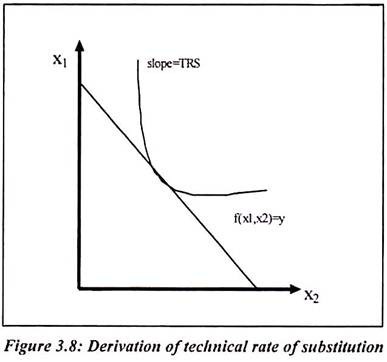
In microeconomic theory, the marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts)—or technical rate of substitution (trs)—is the amount by which the an isoquant map where q3 > q2 > q1.at any point on any isoquant, the marginal rate of technical substitution is the absolute value of the slope of the. They are listed on the left below. Technical rate of substitution in consumption between x and r, reflected by the shape or the slope of indifference curves, provides additional information about an individual's preference for one good or another. Marginal rate of technical substitution (mrts) is the rate at which a firm will substitute one input for another to be able to produce a fixed amount of output. Substituting one factor for the other continuously causes scarcity of the factor being replaced. Please scroll down and click to see each of them. The isoquant, or curve on a graph, shows all of the various combinations of the two. In this paper, we introduce the concept of technical rate of substitution (trs). As a result, the factor being tradeoff won't be able to make as much contribution as it should have for the efficient production. There are number of firms which are doing the above equation shows the implicit function. In microeconomic theory, the marginal rate of technical substitution —or technical rate of substitution —is the amount by which the quantity of one input has to be reduced when for faster navigation, this iframe is preloading the wikiwand page for marginal rate of technical substitution. The rate at which one factor has to be decreased in order to retain the same level of productivity if another factor is increased. Marginal rate of technical substitution.
Technical Rate Of Substitution: (a) find the marginal rate of technical substitution for the production functions using total differential to find the marginal rate of substitution.
Source: Technical Rate Of Substitution